
News
10 03, 2020




































































































.jpg?width=600&name=Mockup-Multinational%20(1).jpg)









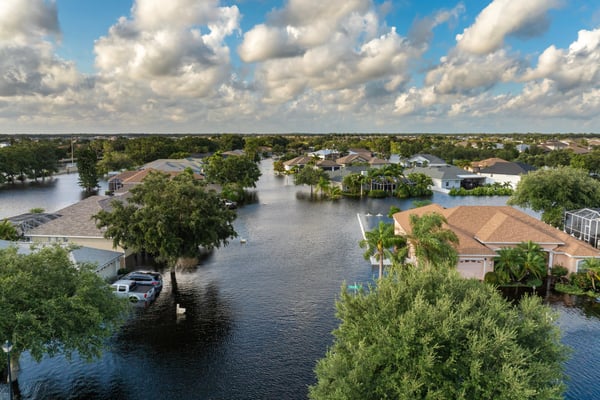
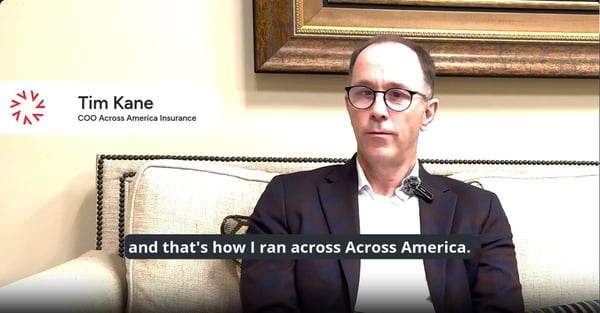
The insurance industry stands at a technological crossroads, where the buzz surrounding Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) is louder than the crowds at Insurtech Insights. AI's promise to revolutionise the sector is immense, offering insurers a ...



























.jpg?width=600&name=Mockup-Multinational%20(1).jpg)






UI Lead

Digital and Technical Training Manager

Finance Manager

PMO Manager

Senior Sales Representative

Director Life & Health

Delivery Lead
.jpg?width=600&name=business-strategy-analysis-and-investment-planning-2025-06-04-17-16-57-utc(1).jpg)
Senior Business Analyst

Interim Head of TPS







Join the global insurers usurping the competition with market-differentiating products and customer service.